Introduction
Groundwater, a vital resource for agriculture, plays a crucial role in sustaining food production and supporting rural livelihoods. Its significance stems from its ability to provide a reliable water supply, especially in regions where surface water is scarce or unreliable. This article explores the importance of groundwater in agriculture, its benefits, challenges, and the sustainable practices needed for its future.

Img Src:-WIkipedia
Groundwater: Definition and Sources
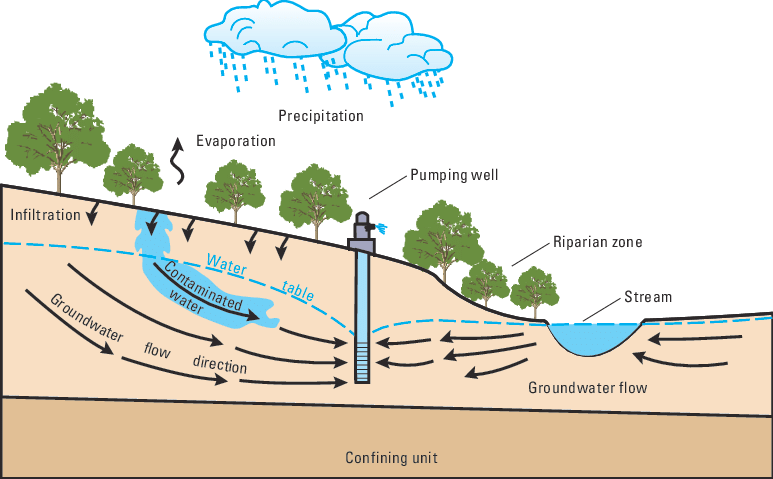
Groundwater refers to water that is found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand, and rock. It originates from precipitation that infiltrates the ground and accumulates in aquifers, which are underground layers of rock or sediment that hold water. Groundwater can be accessed through wells and springs, making it a valuable source of water for various purposes, including agriculture.
Groundwater in Agriculture
Throughout history, groundwater has played a significant role in agriculture, allowing civilizations to thrive in arid and semi-arid regions. Today, groundwater remains essential for agriculture, especially in regions where surface water sources are limited. Its use in agriculture includes irrigation, livestock watering, and crop cultivation, making it indispensable for food production.
Benefits of Groundwater in Agriculture
One of the main advantages of using groundwater in agriculture is its reliability, as it is less susceptible to seasonal fluctuations compared to surface water sources. Groundwater can also improve crop yields and quality, especially in areas prone to drought. Additionally, groundwater can be used for livestock watering, ensuring the health and well-being of animals.
Challenges and Issues
Despite its benefits, groundwater use in agriculture faces several challenges. Over-extraction of groundwater can lead to depletion of aquifers, resulting in reduced water availability and increased pumping costs. Moreover, groundwater quality can be affected by contamination from agricultural activities, posing health risks to both humans and the environment.
Img Src:-researchgate.net
Sustainable Use of Groundwater
To ensure the sustainable use of groundwater in agriculture, conservation methods and recharge techniques are essential. Conservation methods, such as improving irrigation efficiency and reducing water waste, can help minimize groundwater depletion. Recharge techniques, such as artificial recharge and rainwater harvesting, can help replenish groundwater levels.
Future Prospects
Advancements in technology, such as remote sensing and precision agriculture, hold promise for improving groundwater management in agriculture. Additionally, policy interventions, such as groundwater regulation and water pricing, can help incentivize sustainable groundwater use. By adopting these approaches, the future of groundwater in agriculture can be more secure.

Conclusion
In conclusion, groundwater plays a vital role in agriculture, serving as a reliable water source for irrigation, livestock watering, and crop cultivation. However, sustainable practices are crucial to ensure the long-term availability and quality of groundwater. By implementing conservation methods and recharge techniques, the agricultural sector can continue to benefit from groundwater while safeguarding this precious resource for future generations.
Click Here For Interesting Articles and Blogs
FAQs
- What is the main advantage of using groundwater in agriculture? Groundwater is a reliable water source, less susceptible to seasonal fluctuations compared to surface water.
- How can farmers protect groundwater quality? Farmers can protect groundwater quality by using environmentally friendly farming practices and properly managing agricultural inputs.
- Are there regulations for groundwater use in agriculture? Yes, many countries have regulations in place to manage groundwater use in agriculture and protect groundwater resources.
- Can groundwater depletion be reversed? Groundwater depletion can be reversed through sustainable management practices, such as recharging aquifers and reducing water use.
- What role does climate change play in groundwater availability? Climate change can affect groundwater availability by altering precipitation patterns and increasing evaporation rates, potentially leading to changes in groundwater levels.