Soil moisture, often referred to as soil water content, is a critical factor in agriculture and the environment. It is the amount of water present in the soil, which is essential for plant growth, soil health, and various ecosystem functions. Understanding soil moisture and its management is crucial for sustainable agricultural practices and environmental conservation.
What is Soil Moisture?
Soil moisture refers to the water content present in the soil. It plays a vital role in plant growth, as plants absorb water from the soil through their roots. Soil moisture also affects soil structure and nutrient availability, influencing overall soil health.

Factors Affecting Soil Moisture
Several factors influence soil moisture levels, including climate, soil composition, vegetation cover, and human activities.
- Climate: Temperature and precipitation patterns determine the amount of moisture in the soil.
- Soil Composition: Soil texture and structure affect water retention and drainage.
- Vegetation: Plants absorb water from the soil, impacting soil moisture levels.
- Human Activities: Land use practices such as agriculture and deforestation can alter soil moisture content.
Measuring Soil Moisture
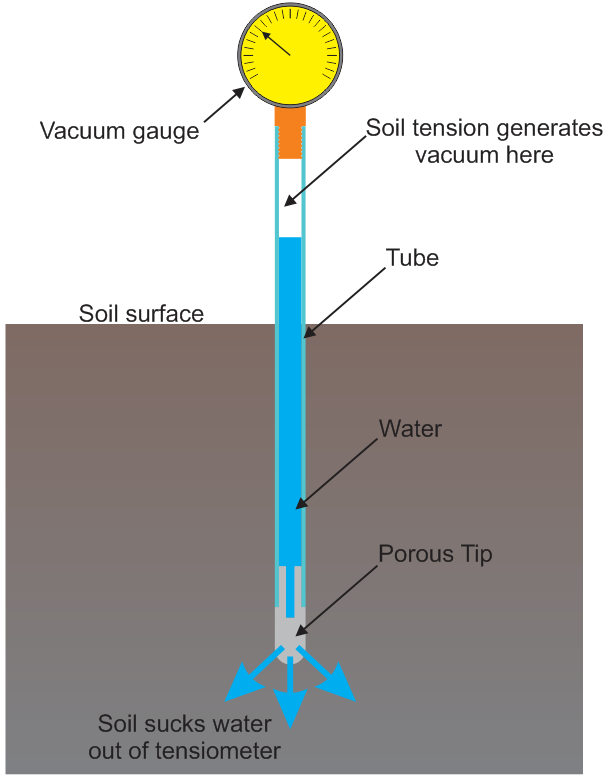
Img Src:-soilmoisture.wordpress.com
Various techniques and instruments are used to measure soil moisture. Common methods include gravimetric analysis, soil moisture sensors, and satellite remote sensing.
Importance of Soil Moisture in Agriculture
Soil moisture is crucial for agriculture, as it directly affects plant growth and crop yields. Adequate soil moisture promotes seed germination, nutrient uptake, and overall plant health. Proper management of soil moisture is essential for irrigation planning and soil conservation practices.
Effects of Soil Moisture on Environment
Soil moisture plays a significant role in environmental processes. It influences climate patterns, as soil moisture levels affect evaporation and transpiration rates. Changes in soil moisture can also impact ecosystem health, including plant and animal habitats.
Managing Soil Moisture
To maintain soil moisture levels, various conservation practices and irrigation strategies are employed. Conservation practices such as cover cropping and mulching help retain soil moisture, while efficient irrigation systems reduce water wastage.

Conclusion
Soil moisture is a critical component of soil health, agriculture, and the environment. Understanding the factors affecting soil moisture and implementing appropriate management practices is essential for sustainable land use and environmental conservation.
Click Here For Information and Latest News Articles
FAQs
- How does soil moisture affect plant growth?
- Soil moisture is essential for plant growth as it provides water and nutrients to the roots. Insufficient moisture can lead to wilting and poor growth.
- What are some common methods to measure soil moisture?
- Common methods include using soil moisture sensors, gravimetric analysis, and satellite remote sensing.
- How can farmers improve soil moisture retention?
- Farmers can improve soil moisture retention by using conservation practices such as mulching and cover cropping.
- Is soil moisture linked to climate change?
- Yes, changes in soil moisture levels can impact climate patterns, including precipitation and temperature.
- What are the consequences of low soil moisture?
- Low soil moisture can lead to drought conditions, reduced crop yields, and soil erosion.